In the tranquil world of ponds and marshes, a peculiar dance between two seemingly unrelated creatures unfolds ducks and frogs. Ducks are known for their charming quacks and graceful waddles frogs evoke images of croaks in the night and agile leaps.
This peaceful coexistence lies a Do Ducks Eat Frogs enigmatic query delves beyond mere instinctual appetites, unveiling a fascinating tale of predator-prey dynamics, ecological balance, and the intricate web of nature’s interconnectedness.
Do Ducks Eat Frogs?
Despite their innocent appearance, ducks are cunning predators when it comes to satisfying their hunger. With their versatile diet, they do not discriminate against frogs, viewing them as just another meal in their quest for sustenance.
The natural instinct of a duck is to seize any opportunity for food, and if a frog happens to cross its path, it will become an easy target. This predatory behaviour showcases the survival instincts deeply ingrained within the duck species, highlighting their ability to adapt and thrive in various environments.
The relationship between ducks and frogs reminds us of the harsh realities of nature, where survival often takes precedence over camaraderie.
A fairytale may depict a more harmonious connection between these creatures, but the truth is far more complex and unforgiving. Ducks’ indiscriminate eating habits underscore the brutal but necessary cycle of life in the animal kingdom – where each species must fend for itself to survive.
Do Ducks Eat Toads?
The sight of ducks feasting on small frogs and toads may seem shocking initially, but it is a reminder of their adaptable nature and survival instincts. Traditional food sources run scarce, but ducks quickly explore alternative options, showcasing their resourcefulness in the face of challenges.

This behaviour highlights their opportunistic approach to feeding, demonstrating that they will not hesitate to venture into new territories in search of sustenance. Witnessing ducks actively hunting for frogs portrays a different side to these seemingly docile creatures.
Do Ducks Eat Tadpoles?
It’s a harsh reality of nature that only a fraction of frog eggs survive to adulthood due to various predators like ducks. The calculated choice of ducks to prey on tadpoles rather than fully-grown frogs is fascinating. Tadpoles, being small and defenceless, offer an easy and safe meal for ducks without the risk of choking, unlike adult frogs.
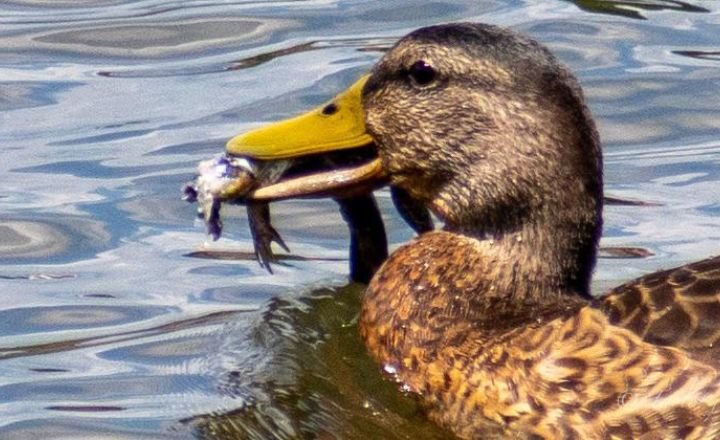

The abundance of tadpoles as duck food highlights the delicate balance in ecosystems. Their vulnerability on the water surface makes them an easy target for opportunistic predators like ducks and hungry birds seeking a quick snack.
This intricately woven relationship between predator and prey showcases the interconnectedness of all living beings in the natural world.
A complex dance of life and death, even tiny creatures like tadpoles play a crucial role in sustaining various species higher up in the food chain. The survival strategies employed by animals like ducks shed light on the constant struggle for existence in the wild, where every decision can mean the difference between life and death.
Food Chain
With their varied diet and unpredictable eating habits, Ducks showcase their adaptability and versatility in the wild. From munching on breadcrumbs in a park to voraciously hunting down frogs in a marshland, these waterfowl exhibit a complex relationship with their food sources.
Their position on the food chain as predators of frogs underscores their role as efficient hunters capable of thriving in diverse environments. Some may find it surprising that ducks have an appetite for frogs, this behaviour sheds light on these seemingly gentle creatures’ natural instincts and predatory traits.
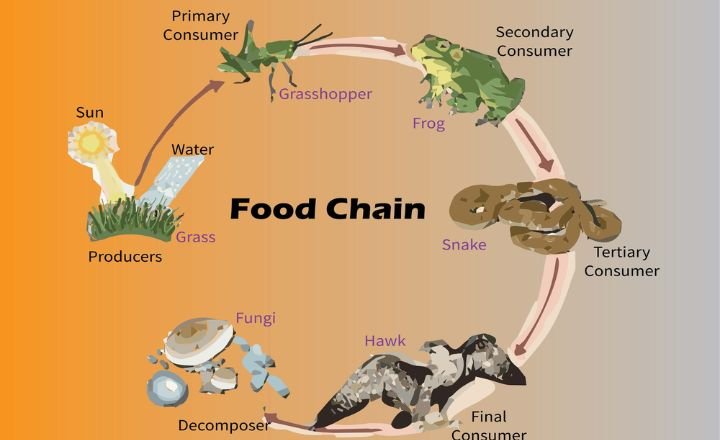
As opportunistic feeders, ducks are crucial in maintaining ecological balance by regulating amphibian populations. This aspect of duck behaviour not only enriches our appreciation for these birds but also illuminates the intricate connections within ecosystems.
Embracing the complexity of nature’s intricacies allows us to glimpse into the fascinating world of animal behaviour and ecological dynamics.
Duck Breeds Hunting Frogs And Toads
Certain duck breeds, such as the Indian Runner and the Pekin, are known to have a penchant for feasting on frogs. This behaviour can be attributed to their hunting instincts and natural ability to catch small prey.
Breeds like the Muscovy and Khaki Campbell excel in pest control by consuming insects and larvae, making them valuable assets for maintaining ecological balance in their surroundings.
The living habitat of ducks greatly influences their food preferences. Ducks that inhabit ponds or rivers tend to have a more natural diet, including aquatic plants and algae.
Mallard Ducks
Mallard ducks are truly impressive hunters. They showcase their agility and tenacity when catching frogs. Their keen eye for spotting prey and quick reflexes make them formidable predators in wetland environments where frogs abound.
Other duck species may struggle to capture fast-moving frogs, but Mallards excel in this skill, making them stand out among their feathered counterparts.

Mallard ducks’ diet reflects their carnivorous nature during the breeding season, as they prioritise acquiring protein-rich food sources like frogs.
Female Mallards exhibit remarkable determination in securing these meaty meals for themselves and their offspring, highlighting their role as skilled providers within the species.
Black Ducks
Black ducks are known for their tenacity when hunting frogs. Their preference for protein-rich diets leads them to engage in prolonged battles with fully-grown frogs.
These encounters can last up to 15 minutes or even half an hour as both parties refuse to back down easily. Frogs’ resilience, clinging to life until the end, adds a fascinating dynamic to this predator-prey interaction.
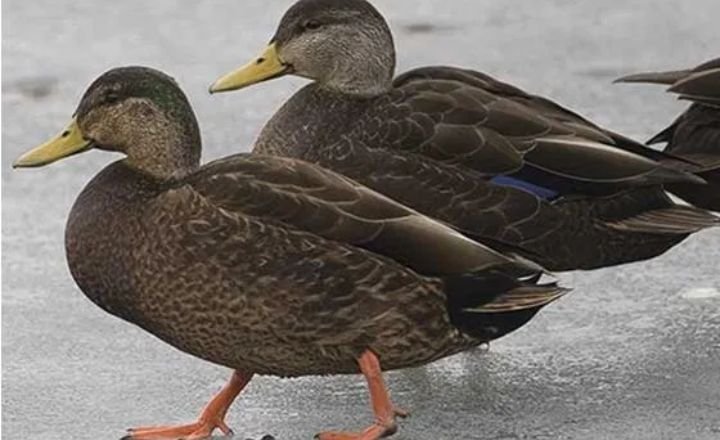

Interestingly, black ducks favour smaller prey like tadpoles due to their size and lack of resistance. Tadpoles present an easy meal option compared to the fierce struggle of hunting larger frogs.
This preference reflects the adaptive nature of these ducks in selecting efficient sources of nutrition from their environment.
How Do Frogs Avoid Being Caught By Ducks?
Frogs have evolved a plethora of defence mechanisms to outsmart their many predators. Their ability to blend seamlessly into their surroundings or swiftly retreat into the water showcases their remarkable adaptability in avoiding becoming a duck’s meal.
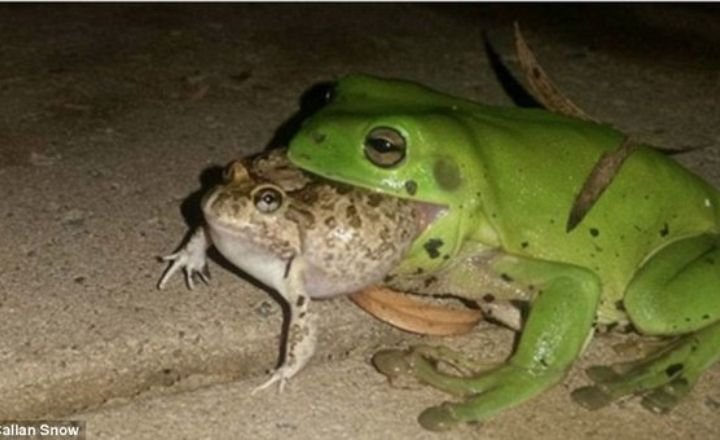

They truly set frogs apart is their unique tactic of secreting distasteful chemicals that make them unpalatable to potential predators like ducks and birds.
The frogs exhibit incredible agility by swiftly climbing high up trees and employing their powerful leg muscles to leap into safety. This quick thinking and physical prowess demonstrate the frog’s capacity for survival under constant threat from predators like ducks.
What do Ducks Eat?
Ducks are known for their diverse and eclectic palate, consuming a wide array of foods like frogs, tadpoles, small fish, and eggs. This varied diet not only provides ducks with essential nutrients but also showcases their adaptability to different environments.
From indulging in snails and molluscs to feasting on crabs, shrimps, and worms, ducks have mastered the art of foraging in both land and water.
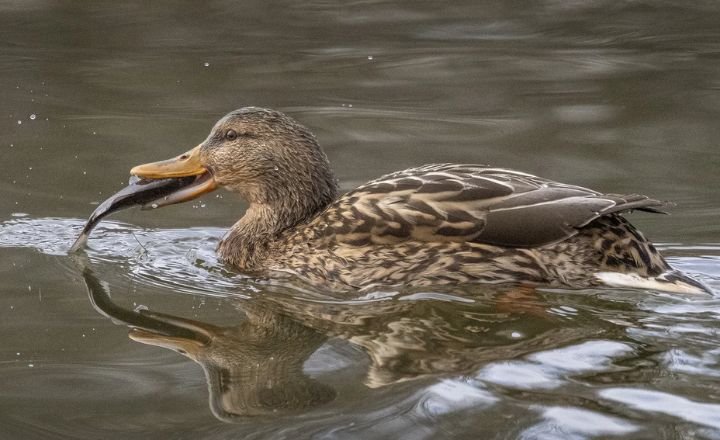

The thought of ducks savouring salamanders, weeds, leaves, seeds, and grasses adds a layer of complexity to their dietary preferences. Their consumption of algae reveals their role as natural recyclers in aquatic ecosystems, while munching on roots and flowers underscores their importance in dispersing seeds.
Conclusion
Do Ducks Eat Frogs is a complex one that requires a nuanced understanding of their diet and behaviour. Ducks are known to consume various types of insects, small fish, and plants. There is limited evidence to suggest that they actively seek out frogs as a primary food source.
In certain circumstances or environments, ducks may opportunistically consume frogs if they encounter them. Research and observation are needed to definitively determine the role of frogs in a duck’s diet.
